President Trump often says the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act has provided “rocket fuel” that will supercharge the US economy. He may, eventually, be right. But economic data for the first months after Congress passed the law shows no evidence of a growth surge.
Here are four figures that tell the story. In each, the dotted line represents Dec. 22, 2017, the day the TCJA became law.
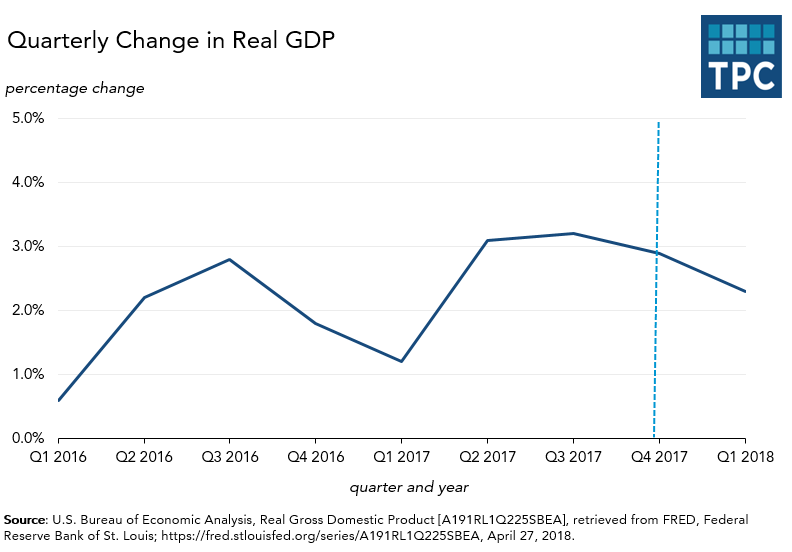
The first shows the growth in real Gross Domestic Product going back to the final year of the Obama Administration. On Friday, the government reported first quarter real GDP grew at an annual rate of 2.3 percent, down from 2.9 percent in the fourth quarter of last year. That’s not far from the average growth rate since the economy climbed out of the Great Recession in 2010 but well short of the 3 percent (or even 4 or 5 percent) annual rate that the president promised.
In fairness, first quarter GDP growth has consistently lagged other quarters in recent years, leading some analysts to wonder if the Bureau of Economic Analysis, which compiles the data, has struggled with seasonal adjustments. It is also important to note that this was BEA’s initial estimate of first quarter growth, a number that is likely to change as it publishes revisions in the coming months.
Beyond the top-line number, take a look at the components of GDP. Consumer spending grew in the first quarter, but at an annual rate of only 1.1 percent. That’s far more slowly than in the fourth quarter of 2017, when it rose by an annual rate of 4%--the strongest showing in three years.
Business investment, by contrast, grew robustly, though also more slowly than in the fourth quarter of 2017. Led by a surge in spending on structures, overall investment rose at an annual rate of 6.1 percent in the first quarter. But that’s only modestly better than 5 percent annual increase in capital investment since 2010. In addition, it is unclear what effect the TCJA had on capital spending since such investments have a very long lead time and were likely planned long before passage of the tax cuts.
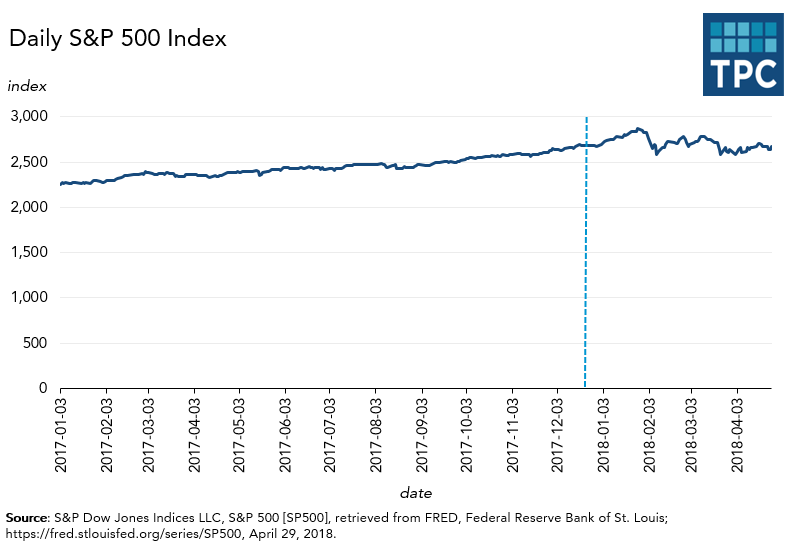
The next figure shows changes in the S&P 500 stock index since January, 2017. The market is one of the president’s favorite metrics. While it has been extremely volatile in recent months, the index ended April not far from where it was before the tax bill was unveiled in early November. Last November 1, just before the initial version of the TCJA was released by House Republicans, the S&P index was 2579. When the market closed on April 30, it sat at 2648, up a modest 2.5 percent over 6 months.
It is impossible to know what drives short-term markets. No doubt, investor euphoria about the tax cuts as well as strong corporate earnings reports helped drive the market boom that ran from early November (as the push for a tax bill began in earnest) through January. Then, perhaps partially due to the president’s threats of a trade war, the market gave back nearly all those gains.
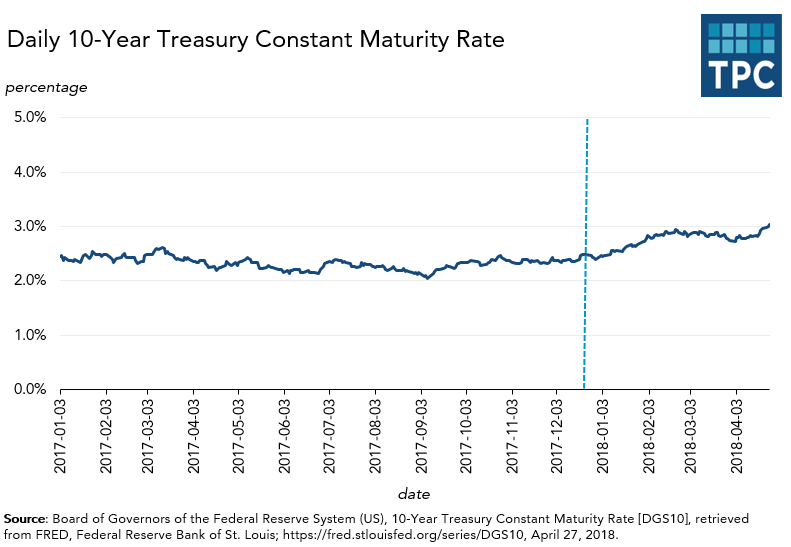
The bond market has been a different story, and a less positive one for consumers and businesses. The third figure shows that yields on the benchmark 10-year Treasury bond rose from 2.33 percent in early November to 2.95 percent on April 30. On April 25, interest rates topped 3 percent, a level many analysts consider a harbinger of inflation. As those higher rates begin to work their way through the economy, it will cost consumers more to buy big ticket items that usually require financing, such as homes and autos. Similarly, some of the benefit of low corporate tax rates will be offset by higher business borrowing costs.
Are higher interest rates a temporary blip, or do they signal market worries about inflation? As with all these other indicators, it is very early. And because the economy is close to full employment, it is not surprising that rates are rising. But the upward trend is worth watching.
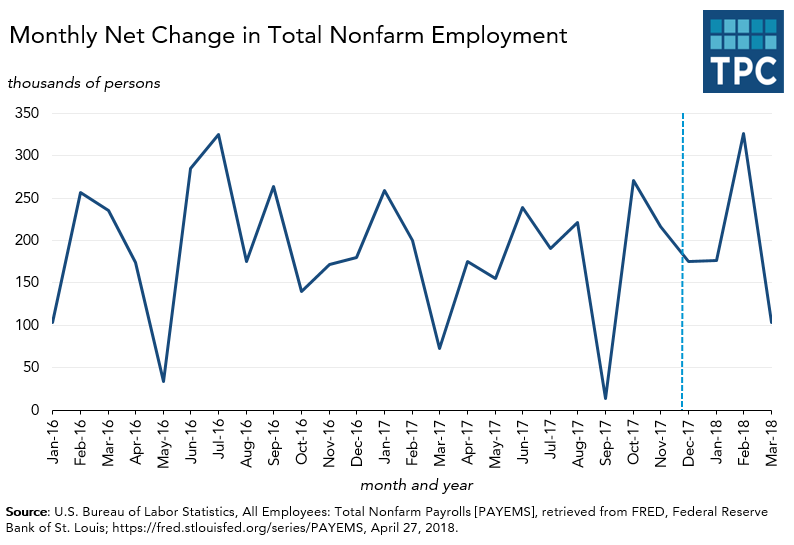
The final figure shows employment—a crucial political metric as well as a key economic measure. The data go back to the last year of the Obama Administration, and despite the predictable month-to-month volatility, the trend has been pretty consistent: The US is creating a net of about 180,000 new jobs each month. That’s what it did before the tax bill was passed and that’s what it has been doing since. For instance, the number of net new non-farm jobs rose by 148,000 in December, 176,000 in January, 326,000 in February and 103,000 in March, or about 188,000-per month over the four-month period.
In other words, it is hard to see an economic inflection point during the tax debate or just after Congress passed the new law. Despite high-profile anecdotes that some businesses would hire in the wake of the tax cuts, no big bump in the long-term employment trend has appeared in the data.
And that, in sum, is the story so far for the TCJA. If it has provided “rocket fuel” for the economy, you can’t see the take-off, at least not yet.
