Last week, President Biden signed the American Rescue Plan (ARP) into law. And the Child Tax Credit (CTC) that began life in 1998 as a benefit of up to $400 for families with children under age 17 now delivers up to $3,600 for each child under age 18.
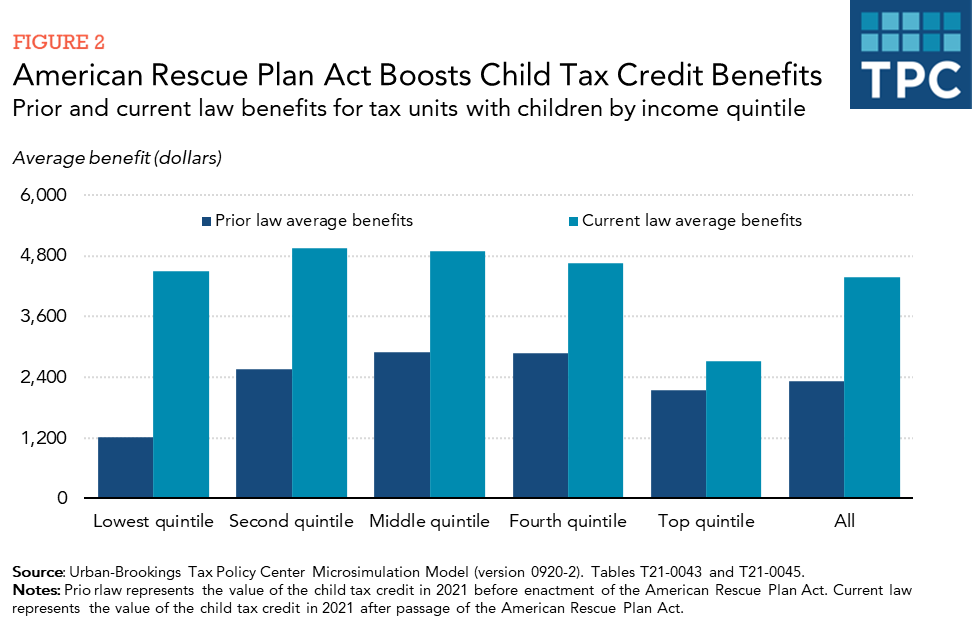
Over 90 percent of all families with children will receive an average benefit of $4,380, according to the Tax Policy Center. And the lowest income families will receive average benefits on par with middle- and high-income families, a departure from how the credit used to work.
The CTC will now deliver more cash support to low-income children than any other federal program, at least for one year.
The ARP changes the way the CTC is calculated in three important ways:
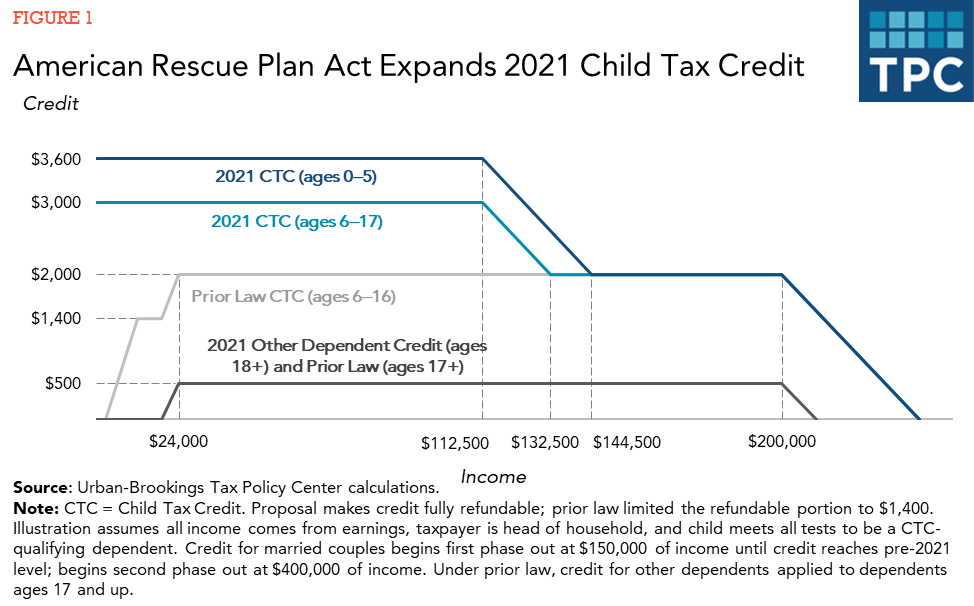
- The maximum credit increases from $2,000 for each child under age 17 to $3,000 for those ages 6 to 17 and $3,600 for younger children.
- The CTC will be fully refundable. Low-income parents will qualify for the full benefit even if they do not work. This piece is key for the lowest income children.
- Children age 17 will be eligible for the refundable benefit. Previously they were allowed no more than $500—the same amount that is still available for families with older children. And it was nonrefundable– it could only be used to offset taxes.
The credit may also be distributed more quickly. Families could start to receive regular payments as early as July. The law is not specific about how frequently the government should make payments. However, it gives the IRS the authority—and some funding—to pay up to half the credit in advance of next year’s tax season. Payments could come monthly or quarterly (but they do not affect the current tax filing season).
Colleagues at the Urban Institute estimate that the advance portion of the CTC alone will reduce the share of children in poverty from 13.7 percent to 11.3 percent. When coupled with other major pieces of the ARPA, child poverty will fall to 6.5 percent – less than half what it is today.
Making the credit fully refundable also will reduce racial disparities among beneficiaries of the full credit – an issue first identified by my colleagues Len Burman and Laura Wheaton in 2005. More recently, Jacob Goldin and Katherine Michelmore found that only half of Black and non-white Hispanic children are eligible for the full CTC under current law, compared to three quarters of white and Asian children.
Removing the earnings requirements from the CTC prevents the tax code from further amplifying racial disparities that exist in employment. The ARP also makes the CTC more widely available to all families in US territories. Previously, the refundable credit was limited to families in Guam, the US Virgin Islands, and the Northern Mariana Islands (mirror code territories). Families in Puerto Rico needed to have three or more children to qualify for benefits of the refundable CTC.
Restricting the refundable portion of the CTC to workers who earned at least $2,500 and limiting the refundable portion of the credit to $1,400 meant that 27 million children lived in families that did not receive the full $2,000 credit because their parents didn’t earn enough under the previous CTC. Benefits, on average, were much lower for families with children in the bottom 20 percent of the income distribution than for those in the middle three income quintiles.
By making the credit fully refundable, the ARP lifts average benefits for the lowest income families (who make $25,000 or less) much closer to those with higher incomes. The credit continues to phase-out for the highest income families, as it did prior to the ARP. However, the enhanced credit phases out more quickly.
Eighteen years ago, Representative Rosa DeLauro (D-CT) first proposed making the CTC fully refundable. Children born then have now outgrown the credit. But the expanded CTC finally achieves Representative DeLauro’s vision of providing substantial benefits to the very lowest income children. At least for 2021.
