National Economic Council chair Larry Kudlow reportedly wants the IRS to redefine capital gains to include only returns from the sale of assets in excess of inflation (or to “index capital gains”). Were it feasible, it would make sense to measure all income and expense in real terms. But indexing capital gains alone by executive fiat while leaving the rest of capital taxation unchanged would make no sense. It would cut capital gains taxes by up to $20 billion a year for the richest Americans and open the door to a raft of new, inefficient tax shelters. And it would do all this without the approval of Congress.
There are a host of problems with applying inflation indexing only to capital gains, but here are the big ones:
- Indexing could be very complex.
- Capital gains are affected less by inflation than other kinds of capital income.
- Indexing capital gains without indexing interest expense and depreciation creates opportunities for tax sheltering.
- Indexing capital gains would add to our burgeoning debt unless accompanied by offsetting tax increases or spending cuts.
- Indexing capital gains alone would be an extremely regressive tax cut.
Indexing capital gains is surprisingly complex
The Administration has not released a specific proposal yet, but past proposals to index capital gains for inflation would multiply the basis (or cost) of capital assets by a factor that represents the increase in the overall price level since purchase. Capital gain would be defined as the difference between the sale price and the indexed basis. This exercise quickly gets complex with additions to basis through, for example, reinvested dividends or new investments in a business. Stock brokers and fund managers would presumably computerize these calculations for publicly traded securities, but tracking indexed basis for nonfinancial assets such as businesses and real estate would be challenging. (The new tax law would simplify these calculations because investments eligible for expensing have a basis of zero). Typically, indexing adjustments are limited to the amount of nominal gain and may not be used to turn a gain into a loss for tax purposes.
Capital gains are less burdened by inflation than other forms of capital income
Because capital gains aren’t taxed until you sell an asset, inflation is a smaller portion of your gain than it is for income that is taxed annually such as interest, rents, and dividends. To see why, think about two investments: a $1,000 bond that pays 4% interest per year and $1,000 painting that appreciates by 4 percent annually. Assume inflation is 2 percent. For the bond, half the $40 annual coupon payment (which is taxable income) is inflation. By contrast, the painting would be worth $1,480 after 10 years. Of that $480 gain, $219 or 45.6% is attributable to inflation.
The inflation share declines as the holding period increases for the capital gains asset, but not for the bond.
Indexing capital gains while leaving capital expense unindexed will fuel more tax shelters
Inflation overstates both capital gains and capital expenses such as interest and depreciation. If taxable gains are discounted while capital expenses are fully deductible, smart taxpayers will be able to generate large paper losses. This already occurs because of the lower tax rates on long-term capital gains. The tax law includes provisions to limit this kind of tax arbitrage, but those guardrails are already wobbly and capital gans indexing would make even more tax shelter schemes profitable.
Indexing capital gains would add to our ballooning budget deficits
Based on IRS data for 2012, the most recent year available, about 1/3 of reported long-term capital gains were attributable to inflation. Treasury estimated long-term capital gains tax revenues of $82.8 billion in that year, so full indexing would have excluded about $27 billion from taxation.
Because indexing proposals typically do not allow nominal gains to be converted into losses and since taxpayers would likely sell more assets if their effective tax rates were cut, the revenue loss might be smaller. But taxpayers could also increase the revenue cost by taking advantage of new sheltering opportunities. On balance, I’d guess that indexing would reduce annual revenues by $10 billion-20 billion per year.
Some commentators have noted that the cost is small relative to the projected $1 trillion annual deficits, but that seems daft. As Will Rogers said, when you find yourself in a hole, the first thing to do is stop digging.
Indexing capital gains is an extremely regressive tax break
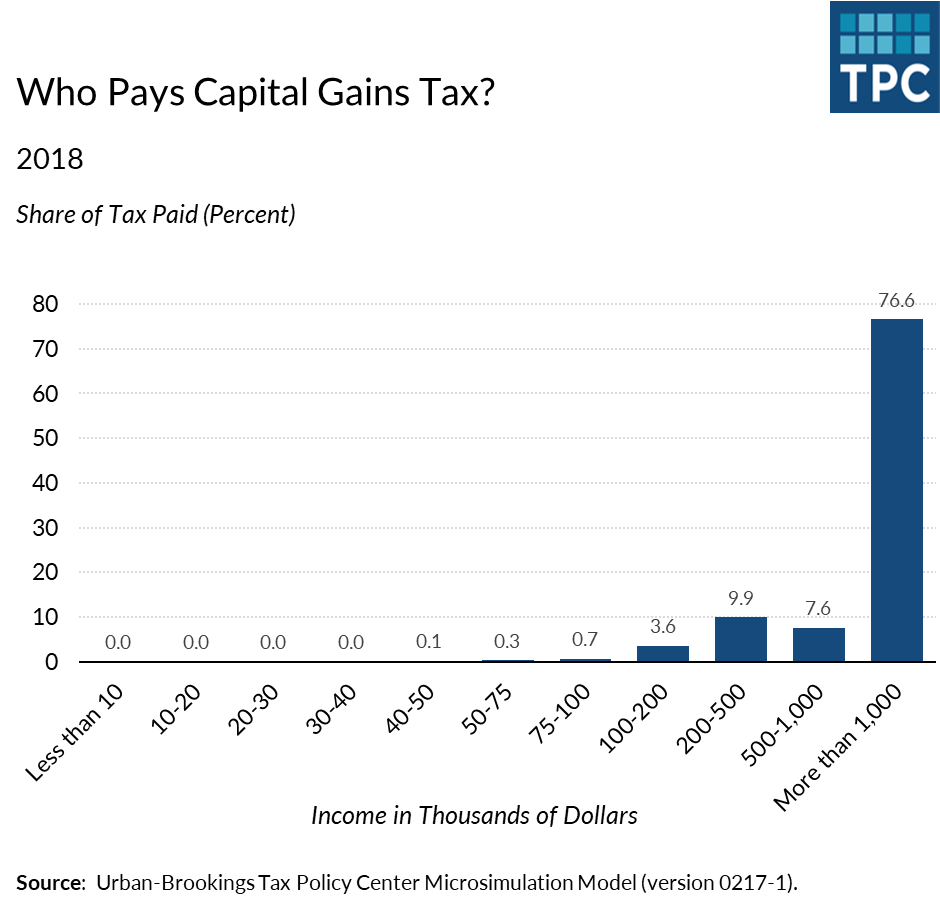
Very rich people hold most assets with capital gains. Therefore, the most well-off would reap the largest benefits from a policy change to index the basis of capital assets. See chart. Congress and President Trump just gave them a big tax cut—and added nearly $2 trillion to the debt over the next decade. There is no reason why they should get yet another windfall.
At first glance, indexing capital gains for inflation may seem like a good idea. But the closer you look, the worse it is. If President Trump really wants to cut taxes on capital gains, he should go to Congress with a plan to do so directly, and not through a poorly designed back-door regulatory scheme.
