The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) significantly changed how families with children were treated under the individual income tax, but for many, changed what they owed in taxes very little.
The (TCJA) doubled the child tax credit (CTC) from $1,000 per child under 17 to $2,000. It also added a $500 credit for older children and other dependents, eliminated the personal exemption for dependents, and made several other changes affecting families with children.
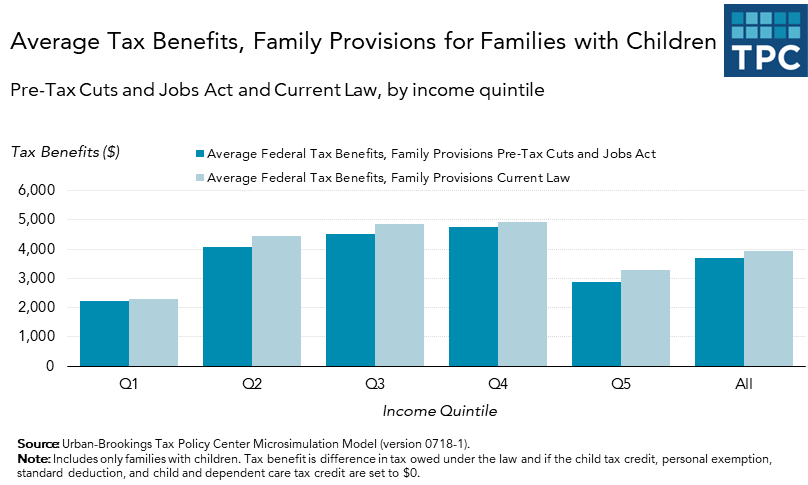
Taken as a whole, the TCJA did reduce near-term taxes for most households. But the provisions intended to broadly subsidize families--the personal exemption, the CTC, the standard deduction, and the child and dependent care tax credit--kept benefits roughly constant between the old and new law.
Keep in mind that many of the individual income tax changes in the TCJA expire after 2025. When they do, families with children can expect to pay more in taxes than they would have if Congress had not changed the law.
The biggest TCJA increase in benefits for families with children came from its doubling of the CTC. Families use this credit to first offset income taxes owed. If the credit exceeds their tax liability, families may receive up to $1,400 per child as a refund—an increase of $400 from prior law. Families now can receive the refundable portion of the credit once their income reaches $2,500 compared to $3,000 under prior law. For some very low-income families that can mean an extra $75 per year.
Somewhat higher-income families were kept from receiving the full value of the credit because they owe less than $600 per child in income taxes (computed as the $2,000 maximum CTC less the $1,400 refundable component). Roughly 27 million children under age 17 live in families who do not earn enough to receive their full $2,000 per child CTC. Benefits for many families are higher than under prior law but fall short of the maximum $1,000 benefit increase.
Middle- and high-income families who owe enough tax to benefit from the full $2,000 per child CTC also benefitted from the increase in the standard deduction as well as from individual income tax rate cuts. But some of those tax cuts were partially offset by the elimination of the personal exemption. Under the pre-TCJA law, families had been allowed to deduct a little over $4,000 per child from taxable income.
On average, families with children in the lowest one-fifth of the income distribution received $60 in additional tax benefits under the family provisions in the TCJA, while families with children in the highest one-fifth of the income distribution received an average of about $390. (See figure below).
Somewhat surprisingly, the TCJA did not increase the earned income tax credit (EITC), even though both Democrats and Republicans backed such a change. But that clearly was not a goal of this tax overhaul, which tilted benefits toward higher-income people.
Should most individual provisions of the TCJA expire as scheduled after 2025, the CTC will return to $1,000 per child and the personal exemption will be restored. However, as with the rest of the tax system, personal exemptions, the standard deduction, and the EITC will grow more slowly since the TCJA included a more conservative--and permanent--measure of inflation. The Tax Policy Center estimated that as a result, taxes for a single parent earning $30,000 with two or fewer children would but rise relative to prior law in 2027.
The TCJA missed an opportunity to provide substantial additional support to families with children. Rather, the law changed the amount of family benefits by very little, though higher-income families benefited slightly more than lower-income families.
A version of this blog post was originally posted as part of the AEI blog series “Trump’s Tax Reform Happened, now what?"
