Until the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), people across the income distribution could say they benefited from the tax code’s many targeted tax benefits. But, according to a new analysis by the Tax Policy Center, the benefits of many itemized deductions have shifted from middle-income households to those with higher incomes.
The change was largely driven by two elements of the TCJA: Its increase in the standard deduction and its $10,000 cap on the state and local tax deduction. Combined with other changes, they resulted in a big decline in the number of people itemizing deductions.
That shift in turn has important implications for the political sustainability of some popular tax subsidies. For instance, will deductions for mortgage interest and charitable giving survive once voters--and lawmakers—realize they increasingly have become cash cows primarily for the wealthy?
The mortgage deduction
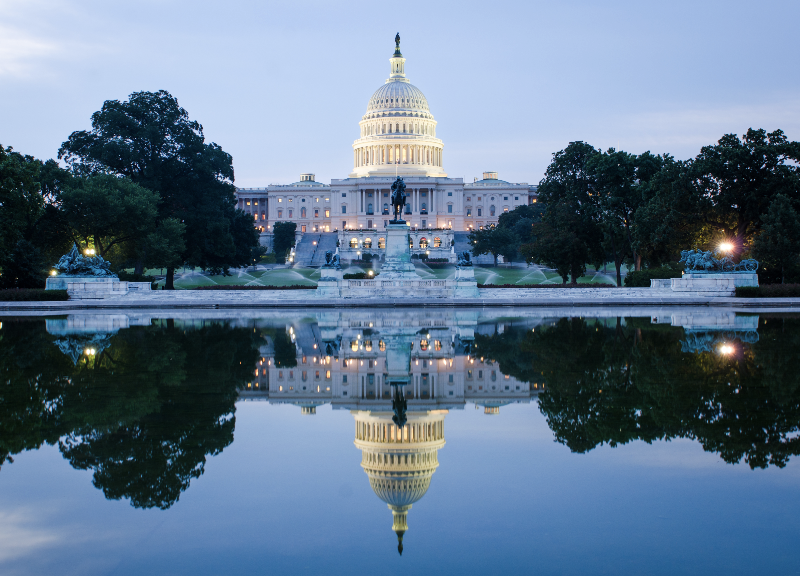
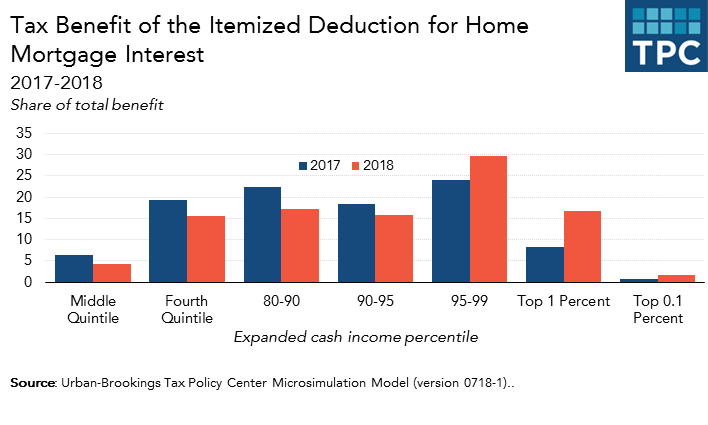
For example, in 2017 about 16 percent of middle-income households (those making between about $49,000 and $85,000), benefited from the mortgage interest deduction (MID). In 2018, fewer than 5 percent will receive any benefit from the MID. Overall, middle-income households received about 6.4 percent of the total tax benefit of the MID in 2017 but will get one-third less, only 4.3 percent, in 2018. These effects would reverse after 2026 should the TCJA’s individual income tax changes expire as scheduled.
Take a look at households in the 80th-90th slice of the income distribution, those who made between $152,000 and $220,000 last year. Even their share of benefits from the MID has collapsed. Last year, almost two-thirds took the mortgage deduction. This year, fewer than one-quarter will. Their overall share of the tax break will fall from 22.4 percent in 2017 to 17.1 percent this year.
Where are those benefits going? Much is landing in the pockets of those in the 95th-99th percentile (who make between $315,000 and $745,000). Their share of MID is up from 24 percent in 2017 to almost 30 percent this year.
Charitable giving
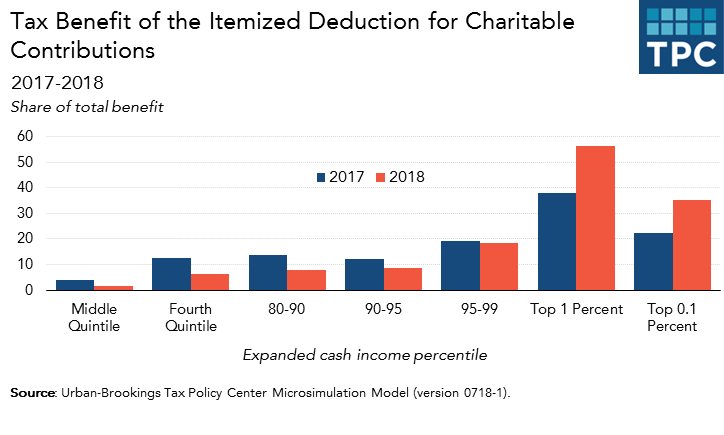
It the same story with charitable giving. Last year, about 16 percent of middle-income households got a charitable deduction. This year only about 5 percent will claim the deduction. Those with middle-incomes already received a very small share of the tax benefit—only about 3.8 percent last year—but in 2018 their share will be less than half that—1.6 percent.
Even households in the 80th-90th percentile will lose the benefit of the charitable deduction. The percentage receiving any tax break at all will fall from about 64 percent to about 24 percent. The group’s overall share of the charitable tax break will fall from about 14 percent to just 8 percent.
The benefit of the charitable deduction shifts even higher up the income distribution than the MID does. Households in the top 1 percent, who made $745,000 or more last year, received about 40 percent of the value of the deduction last year. This year, they’ll get 56 percent.
Shifting SALT
The state and local tax (SALT) deduction tale is more complicated. A smaller fraction of middle-income households will claim the SALT deduction, though that income group will get a slightly larger share of the overall tax benefit. In 2017, about 22 percent of middle-income households took the SALT deduction. This year, just over 6 percent will. However, their overall share of the benefit will rise slightly, from 4.6 percent to 5.2 percent, largely due to the TCJA’s $10,000 cap on the SALT deduction which limits the amount that many high-income taxpayers can deduct.
The policy effects of these changes could be profound. For example, deductions for mortgage interest and charitable giving were always debatable on efficiency and equity grounds since they subsidize activities that may have occurred anyway and provide the largest benefits to those with the highest incomes (and the highest marginal tax rates). Even if you believe that subsidizing these activities is a good idea, the current deduction was a poor way to do it even before the TCJA.
Shifting politics
But now, one wonders if the politics will shift as well. How much political support will the mortgage deduction generate if fewer than 5 percent of middle-income households benefit from it, and if only one-quarter of even upper-middle income households take it? Can the non-profit sector sustain a deduction for charitable giving when less than 2 percent of the benefit goes to middle-income households and three-quarters goes to the highest-income 5 percent?
I doubt Congress intended to so profoundly change the nature of tax deductions through the TCJA—or if many lawmakers who voted for the law were even aware of what they did. But whether they knew it or not, they may have just opened the door to even bigger changes in the way we use tax policy to subsidize a long list of economic activities.
